Inferring food intake from multiple biomarkers using a latent variable model.
Silvia D’Angelo, Lorraine Brennan, and Isobel Claire Gormley (2021).
Annals of Applied Statistics.
Metabolomic-based approaches have gained much attention in recent years, due to their promising potential to deliver objective tools for assessment of food intake. In particular, multiple biomarkers have emerged for single foods. However, there is a lack of statistical tools available for combining multiple biomarkers to quantitatively infer food intake. Furthermore, there is a paucity of approaches for estimating the uncertainty around biomarker-based inferred intake.
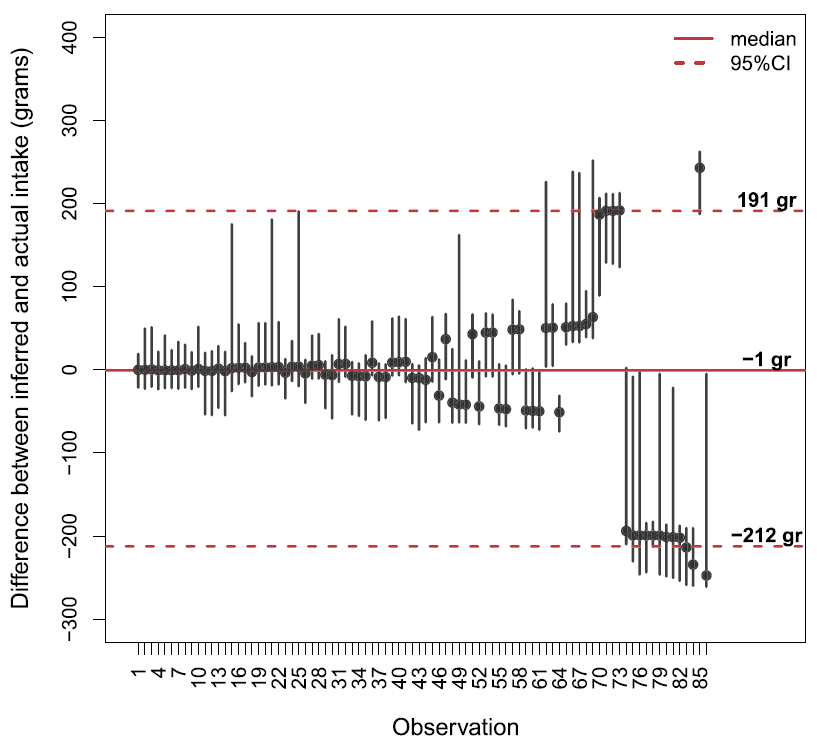
Here, to estimate the relationship between multiple metabolomic biomarkers and food intake in an intervention study conducted under the A-DIET research programme, a latent variable model, multiMarker, is proposed. The multiMarker model integrates factor analytic and mixture of experts models: the observed biomarker values are related to intake which is described as a continuous latent variable which follows a flexible mixture of experts model with Gaussian components. The multiMarker model also facilitates inference on the latent intake when only biomarker data are subsequently observed. A Bayesian hierarchical modelling framework provides flexibility to adapt to different biomarker distributions and facilitates inference of the latent intake along with its associated uncertainty.
Simulation studies are conducted to assess the performance of the multiMarker model, prior to its application to the motivating application of quantifying apple intake.